Dijkstra算法
迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法是典型最短路径算法,用于计算一个节点到其他节点的最短路径。 它的主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展(广度优先搜索思想),直到扩展到终点为止。
本文将使用Java实现使用Dijkstra算法对带权有向图的最短路径查找。
关于图的创建及其相关操作,可移步:数据结构之图及其遍历(Java实现)
本文使用的带权有向图:
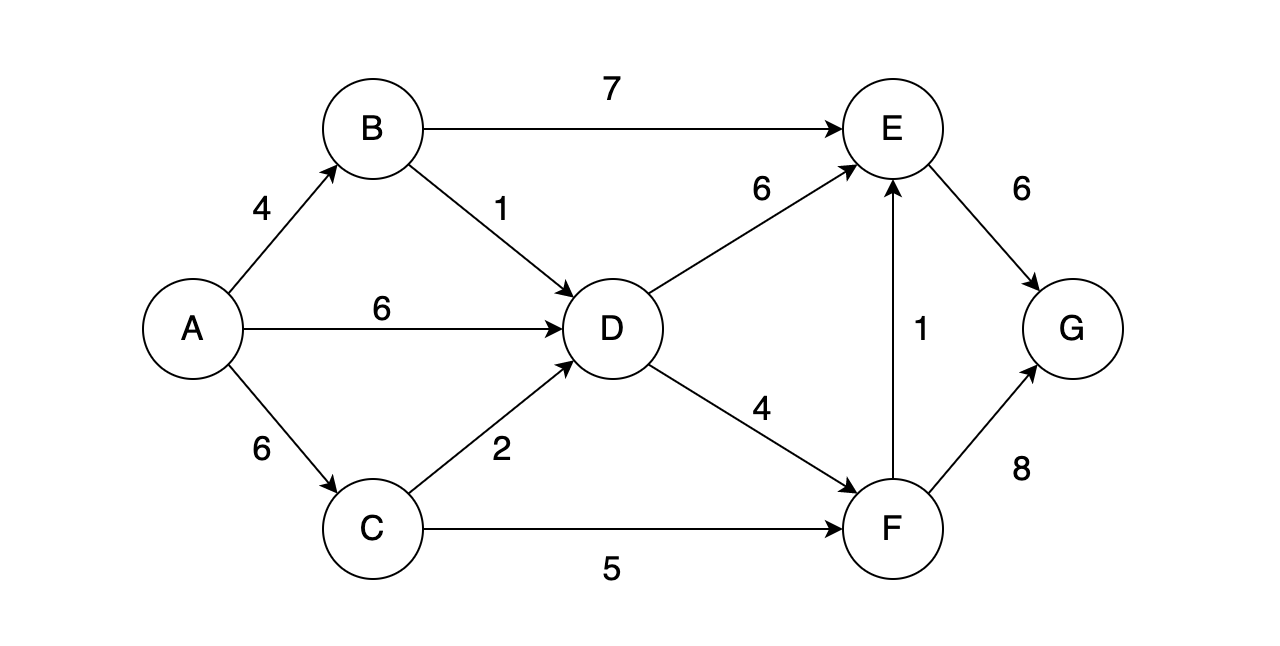
算法详解
Dijkstra算法,是查询某一点,到图中所有可达点的最短路径的算法,本文以A点为例。
首先,我们需要准备几个数组(本文将索引抽象为字母方便理解),用于记录如下数据:
- 某节点的前驱结点数组,用于结果的回溯:pre[]
- 记录当前最短距离的数组:distance[]
- 记录是否标记位为最短路径的数组:ok[]
如下表:
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| distance[] | |||||||
| ok[] | |||||||
| pre[] |
初始时,A点到所有点的距离都为∞,前驱结点都不存在,都不是最短距离:
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| distance[] | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ |
| ok[] | false | false | false | false | false | false | false |
| pre[] | null | null | null | null | null | null | null |
第一轮,首先将A点可达点记录下来,找到距离最短的点B,标记位最短,更新数据
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| distance[] | ∞ | 4 | 6 | 6 | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ |
| ok[] | false | true | false | false | false | false | false |
| pre[] | null | A | A | A | null | C | null |
接下来,在未被标记节点中,找到最小的路径,即C,从该点出发,找到C的可达点,更新距离数据(若距离相加大于原距离则不更新)、前驱结点和标记最短路径
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| distance[] | ∞ | 4 | 6 | 6 | ∞ | 11 | ∞ |
| ok[] | false | true | true | false | false | false | false |
| pre[] | null | A | A | null | null | C | null |
重复上述操作,直至所有点都被标记为最短路径:
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| distance[] | 0 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 10 | 9 | 16 |
| ok[] | true | true | true | true | true | true | True |
| pre[] | null | A | A | B | F | D | nulE |
如何找到最短路径:
根据前驱结点数组回溯即可
代码实现
查找最小索引
// 获取没有标记的最小值索引
private int getMinIndex(int[] dist, boolean[] ok) {
int minIndex = -1;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < dist.length; i++) {
if (min > dist[i] && !ok[i]) {
minIndex = i;
min = dist[i];
}
}
return minIndex;
}算法实现
// Dijkstra搜索最短路径
public LinkedList<Integer> dijkstra(int from, int to) {
int infinity = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 距离无穷
int[] pre = new int[getNumOfVertex()]; // 前驱结点数组
int[] distance = new int[getNumOfVertex()]; // 记录距离值
boolean[] ok = new boolean[getNumOfVertex()]; // 记录是否标记
Arrays.fill(pre, -1); // 初始前面点均为-1,即不可达
Arrays.fill(distance, infinity); // 初始时都为无穷
distance[from] = 0; // 起点到起点距离为0
// 跳出循环条件,最小值不等于-1,即还存在最小值
while (getMinIndex(distance, ok) != -1) {
int minIndex = getMinIndex(distance, ok); // 找到最小
ok[minIndex] = true; // 标记之
for (int i = 0; i < getNumOfVertex(); i++) {
int dist = getWeight(minIndex, i);
// 若不等于0,即可达
if (dist != 0) {
// 比较当前距离是否比原先标记更短,若更短
if (distance[i] > distance[minIndex] + dist) {
distance[i] = distance[minIndex] + dist; // 更新最短距离
pre[i] = minIndex; // 更新前驱结点
}
}
}
}
LinkedList<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
int index = to;
while (true) {
index = pre[index];
if (index == -1) {
break;
}
result.addFirst(index);
}
if (result.size() == 0) {
return result;
}
result.addLast(to);
return result;
}测试
package org.kakkk.graph;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph();
graph.addVertex("A");
graph.addVertex("B");
graph.addVertex("C");
graph.addVertex("D");
graph.addVertex("E");
graph.addVertex("F");
graph.addVertex("G");
graph.addAdjacent("A","B",4);
graph.addAdjacent("A","D",6);
graph.addAdjacent("A","C",6);
graph.addAdjacent("B","E",7);
graph.addAdjacent("B","D",1);
graph.addAdjacent("C","D",1);
graph.addAdjacent("C","F",5);
graph.addAdjacent("D","E",6);
graph.addAdjacent("D","F",4);
graph.addAdjacent("E","G",6);
graph.addAdjacent("F","E",1);
graph.addAdjacent("F","G",8);
graph.dijkstra("A","G");
}
}输出:
ABDFEG复合预期
完整代码
Graph.java
package org.kakkk.graph;
import java.util.*;
public class Graph {
private Map<String, Integer> vertex2Index; // 节点到索引的转换
private Map<Integer, String> index2Vertex; // 索引到节点的转换
private Set<String> vertex; // 节点Set
private int maxIndex; // 最大索引
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adjacent; // 邻接矩阵
public Graph() {
this.vertex = new HashSet<>();
this.vertex2Index = new HashMap<>();
this.index2Vertex = new HashMap<>();
this.adjacent = new ArrayList<>();
this.maxIndex = -1;
}
// 插入顶点
public boolean addVertex(String vertex) {
if (this.vertex.contains(vertex)) {
return false;
}
this.vertex.add(vertex);
maxIndex++;
this.vertex2Index.put(vertex, maxIndex);
this.index2Vertex.put(maxIndex, vertex);
// 扩大邻接矩阵
// 列
for (ArrayList<Integer> list : this.adjacent) {
list.add(0);
}
// 行
this.adjacent.add(new ArrayList<>(10));
for (int i = 0; i < this.adjacent.size(); i++) {
this.adjacent.get(this.adjacent.size() - 1).add(0);
}
return true;
}
// 插入边
public boolean addAdjacent(String from, String to, int weight) {
// 判断是否存在
if (!(this.vertex.contains(from) && this.vertex.contains(to))) {
return false;
}
// 设置邻接矩阵
this.adjacent.get(this.vertex2Index.get(from)).set(this.vertex2Index.get(to), weight);
return true;
}
// 删除边
public boolean delAdjacent(String from, String to) {
// 判断是否存在
if (!(this.vertex.contains(from) && this.vertex.contains(to))) {
return false;
}
// 设置邻接矩阵
this.adjacent.get(this.vertex2Index.get(from)).set(this.vertex2Index.get(to), 0);
return true;
}
// 删除节点
public boolean delVertex(String vertex){
// 校验是否存在
if (!this.vertex.contains(vertex)) {
return false;
}
int index = this.vertex2Index.get(vertex);
// 删除行
this.adjacent.remove(index);
// 删除列
for(ArrayList<Integer> list:this.adjacent){
list.remove(index);
}
// 索引调整
for (int i = index; i < maxIndex; i++) {
this.index2Vertex.put(index,this.index2Vertex.get(index+1));
}
// 删除节点
this.index2Vertex.remove(maxIndex);
maxIndex--;
this.vertex2Index.remove(vertex);
this.vertex.remove(vertex);
return true;
}
public int getWeight(String from, String to) {
// 判断是否存在
if (!(this.vertex.contains(from) && this.vertex.contains(to))) {
return -1;
}
return this.adjacent.get(this.vertex2Index.get(from)).get(this.vertex2Index.get(to));
}
private int getWeight(int from, int to) {
return this.adjacent.get(from).get(to);
}
public void showAdjacent() {
for (ArrayList<Integer> list : this.adjacent) {
System.out.println(list);
}
}
private int getNumOfVertex() {
return this.vertex.size();
}
// 获取第一个相邻的节点
public int getFirstNeighbor(int index) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.vertex.size(); i++) {
if (adjacent.get(index).get(i) > 0) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 获取相邻的节点的下一个相邻节点
public int getNextNeighbor(int from, int to) {
for (int i = to + 1; i < this.vertex.size(); i++) {
if (adjacent.get(from).get(i) > 0) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public void dfs(boolean[] isVisited, int index) {
System.out.print(this.index2Vertex.get(index));
isVisited[index] = true;
int w = getFirstNeighbor(index);
while (w != -1) {
if (!isVisited[w]) {
dfs(isVisited, w);
}
w = getNextNeighbor(index, w);
}
}
public void dfs() {
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[vertex.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < getNumOfVertex(); i++) {
if (!isVisited[i]) {
dfs(isVisited, i);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public void bfs(boolean[] isVisited, int index) {
int headIndex;
int w;
LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
System.out.print(this.index2Vertex.get(index));
isVisited[index] = true;
queue.add(index);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
headIndex = queue.removeFirst();
w = getFirstNeighbor(headIndex);
while (w!=-1&&!isVisited[w]) {
System.out.print(this.index2Vertex.get(w));
isVisited[w] = true;
queue.add(w);
w = getNextNeighbor(headIndex, w);
}
}
}
public void bfs() {
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[vertex.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < getNumOfVertex(); i++) {
if (!isVisited[i]) {
bfs(isVisited, i);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
// Dijkstra搜索最短路径
public LinkedList<Integer> dijkstra(int from, int to) {
int infinity = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 距离无穷
int[] pre = new int[getNumOfVertex()]; // 前驱结点数组
int[] distance = new int[getNumOfVertex()]; // 记录距离值
boolean[] ok = new boolean[getNumOfVertex()]; // 记录是否标记
Arrays.fill(pre, -1); // 初始前面点均为-1,即不可达
Arrays.fill(distance, infinity); // 初始时都为无穷
distance[from] = 0; // 起点到起点距离为0
// 跳出循环条件,最小值不等于-1,即还存在最小值
while (getMinIndex(distance, ok) != -1) {
int minIndex = getMinIndex(distance, ok); // 找到最小
ok[minIndex] = true; // 标记之
for (int i = 0; i < getNumOfVertex(); i++) {
int dist = getWeight(minIndex, i);
// 若不等于0,即可达
if (dist != 0) {
// 比较当前距离是否比原先标记更短,若更短
if (distance[i] > distance[minIndex] + dist) {
distance[i] = distance[minIndex] + dist; // 更新最短距离
pre[i] = minIndex; // 更新前驱结点
}
}
}
}
LinkedList<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
int index = to;
while (true) {
index = pre[index];
if (index == -1) {
break;
}
result.addFirst(index);
}
if (result.size() == 0) {
return result;
}
result.addLast(to);
return result;
}
// 获取没有标记的最小值索引
private int getMinIndex(int[] dist, boolean[] ok) {
int minIndex = -1;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < dist.length; i++) {
if (min > dist[i] && !ok[i]) {
minIndex = i;
min = dist[i];
}
}
return minIndex;
}
public void dijkstra(String from, String to) {
LinkedList<Integer> result = dijkstra(this.vertex2Index.get(from), this.vertex2Index.get(to));
for (Integer i : result) {
System.out.print(this.index2Vertex.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Main.Java
package org.kakkk.graph;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph();
graph.addVertex("A");
graph.addVertex("B");
graph.addVertex("C");
graph.addVertex("D");
graph.addVertex("E");
graph.addVertex("F");
graph.addVertex("G");
graph.addAdjacent("A","B",4);
graph.addAdjacent("A","D",6);
graph.addAdjacent("A","C",6);
graph.addAdjacent("B","E",7);
graph.addAdjacent("B","D",1);
graph.addAdjacent("C","D",1);
graph.addAdjacent("C","F",5);
graph.addAdjacent("D","E",6);
graph.addAdjacent("D","F",4);
graph.addAdjacent("E","G",6);
graph.addAdjacent("F","E",1);
graph.addAdjacent("F","G",8);
graph.dijkstra("A","G");
}
}